What Language Should I Learn on Duolingo?

Use this quiz to help you choose a language to learn on Duolingo.
What Language Should I Learn on Duolingo?
Writing System

A writing system is a method of visually representing verbal communication. While both writing and speech are useful in conveying messages, writing differs in also being a reliable form of information storage and transfer. Writing systems require shared understanding between writers and readers of the meaning behind the sets of characters that make up a script. Writing is usually recorded onto a durable medium, such as paper or electronic storage, although non-durable methods may also be used, such as writing on a computer display, on a blackboard, in sand, or by skywriting. Reading a text can be accomplished purely in the mind as an internal process, or expressed orally.
What type of writing system do you prefer?







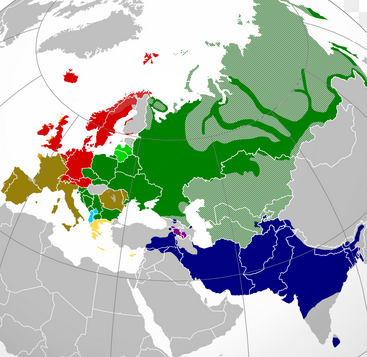
Linguistic Family

A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ancestral language or parental language, called the proto-language of that family. The term "family" reflects the tree model of language origination in historical linguistics, which makes use of a metaphor comparing languages to people in a biological family tree, or in a subsequent modification, to species in a phylogenetic tree of evolutionary taxonomy. Linguists therefore describe the daughter languages within a language family as being genetically related.
What linguistic family do you prefer?











Morphology

In linguistics, morphology is the study of words, how they are formed, and their relationship to other words in the same language. It analyses the structure of words and parts of words, such as stems, root words, prefixes, and suffixes. Morphology also looks at parts of speech, intonation and stress, and the ways context can change a word's pronunciation and meaning. Morphology differs from morphological typology, which is the classification of languages based on their use of words, and lexicology, which is the study of words and how they make up a language's vocabulary.
What type of morphology do you prefer to study?




Number of Speakers

It is not possible to devise a coherent set of linguistic criteria for distinguishing languages in a dialect continuum. For example, a language is often defined as a set of varieties that are mutually intelligible, but independent national standard languages may be considered to be separate languages even though they are largely mutually intelligible, as in the case of Danish and Norwegian. Conversely, many commonly accepted languages, including German, Italian and even English, encompass varieties that are not mutually intelligible. While Arabic is sometimes considered a single language centred on Modern Standard Arabic, other authors describe its mutually unintelligible varieties as separate languages. Similarly, Chinese is sometimes viewed as a single language because of a shared culture and common literary language. It is also common to describe various Chinese dialect groups, such as Mandarin, Wu and Yue, as languages, even though each of these groups contains many mutually unintelligible varieties.
There are also difficulties in obtaining reliable counts of speakers, which vary over time because of population change and language shift. In some areas, there is no reliable census data, the data is not current, or the census may not record languages spoken, or record them ambiguously. Sometimes speaker populations are exaggerated for political reasons, or speakers of minority languages may be under-reported in favour of a national language.
Do you prefer to learn a widely spoken language, or one with fewer speakers?










Number of Learners (on Duolingo)

Do you prefer to go with the crowd, or to belong to a selected group of learners?










Grammatical Gender

In linguistics, grammatical gender is a specific form of noun class system in which the division of noun classes forms an agreement system with another aspect of the language, such as adjectives, articles, pronouns, or verbs. This system is used in approximately one quarter of the world's languages. In these languages, most or all nouns inherently carry one value of the grammatical category called gender; the values present in a given language (of which there are usually two or three) are called the genders of that language. According to one definition: "Genders are classes of nouns reflected in the behaviour of associated words."
Common gender divisions include masculine and feminine; masculine, feminine, and neuter; or animate and inanimate. In a few languages, the gender assignment of nouns is solely determined by their meaning or attributes, like biological sex, humanness, or animacy. However, in most languages, this semantic division is only partially valid, and many nouns may belong to a gender category that contrasts with their meaning, in which case the gender assignment can also be influenced by the morphology or phonology of the noun, or in some cases can be apparently arbitrary.
Do you want to deal with grammatical genders?






Grammatical Cases

Case is a linguistics term regarding a manner of categorizing nouns, pronouns, adjectives, participles, and numerals according to their traditionally corresponding grammatical functions within a given phrase, clause, or sentence. In some languages, nouns, pronouns, adjectives, determiners, participles, prepositions, numerals, articles and their modifiers take different inflected forms, depending on their case. As a language evolves, cases can merge (for instance, in Ancient Greek, the locative case merged with the dative case), a phenomenon formally called syncretism.





Tones

Tone is the use of pitch in language to distinguish lexical or grammatical meaning – that is, to distinguish or to inflect words. All verbal languages use pitch to express emotional and other paralinguistic information and to convey emphasis, contrast, and other such features in what is called intonation, but not all languages use tones to distinguish words or their inflections, analogously to consonants and vowels. Languages that do have this feature are called tonal languages; the distinctive tone patterns of such a language are sometimes called tonemes, by analogy with phoneme. Tonal languages are common in East and Southeast Asia, the Pacific, Africa, and the Americas; as many as seventy percent of world languages may be tonal.
So, how musical do you like your languages?




Tree Length

Each course on Duolingo has its own structure. As they are organised in skills, in a vertical structure, we usually refer to this structure as "skill tree". A shorter tree means a smaller course, which can be completed more quickly but won't give you much proficiency in the target language. A longer skill tree means more content to study, which will probably require more time to complete but will cover more topics and give you a better knowledge of the language.
Do you want a shorter course, just to get an introduction to the language, or a longer course, to really commit to a language?








And Ukrainian is indeed one of the languages I am learning.
Yes! Told me I should learn spanish and I’m already learning it
Ooooh, Ukrainan.
It told me to learn English, my native language.
I’ve ran through the questions several times, told me to learn english twice
It’s my native language
😀